有时候无法直接观察和查看多层网络,可视化是一个很重要的方法
数据可视化
1 | import numpy as np |
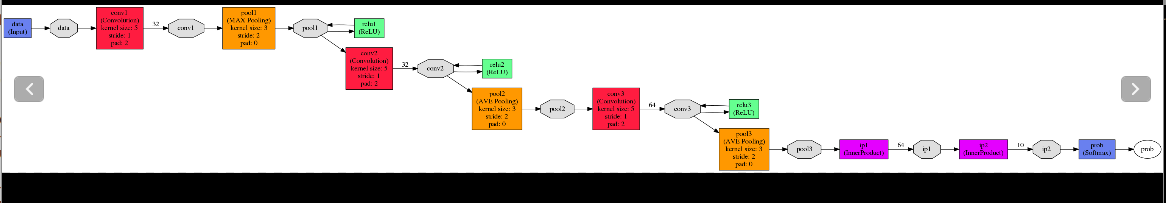
模型可视化
cifar10的网络模型
1 | cd python |
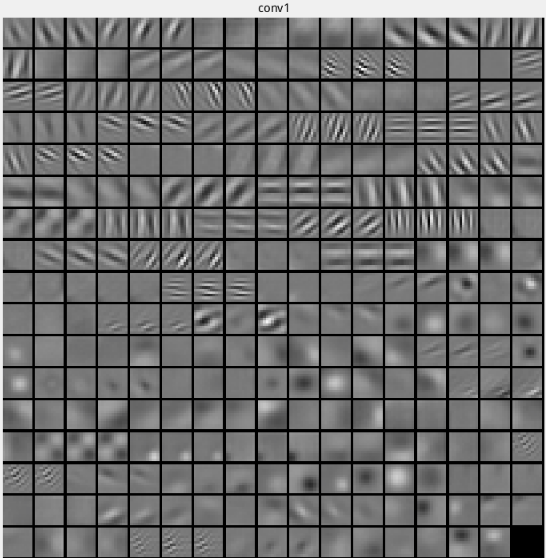
网络权值可视化
对训练后的网络权值进行可视化可以判断模型的优劣及是否欠(过)拟合
经过良好的训练的网络权值通常美观,光滑;反之为噪声图像,或者图案相关性太高,或者缺乏结构性…
进行可视化的代码只需要读取训练后的网络结构和权值文件,将各层的权值数据投影到像素空间.
主程序
1 | clear; |
可视化函数:
1 | function visualize_weight(net,param_name,space) |
结果:
当然每一个卷积层都可以进行可视化
层的特征可视化
在ipython notebook环境下运行
设置环境
1 |
|
下载模型
1 | import os |
下载网络和输入数据
1 | caffe.set_mode_cpu() |
下载处理图片
1 | # load the mean ImageNet image (as distributed with Caffe) for subtraction |
1 | print net.blobs['data'].data.shape |
输出:
1 | (1, 3, 227, 227) |
1 | # set the size of the input (we can skip this if we're happy |
1 | # Load an image (that comes with Caffe) and perform the preprocessing we've set up. |

1 |
|
输出:
1 | predicted class is: 281 |
1 | # 下载标签 |
output label: n02123045 tabby, tabby cat
1 | # for each layer, show the output shape |
data (1, 3, 227, 227)
conv1 (1, 96, 55, 55)
pool1 (1, 96, 27, 27)
norm1 (1, 96, 27, 27)
conv2 (1, 256, 27, 27)
pool2 (1, 256, 13, 13)
norm2 (1, 256, 13, 13)
conv3 (1, 384, 13, 13)
conv4 (1, 384, 13, 13)
conv5 (1, 256, 13, 13)
pool5 (1, 256, 6, 6)
fc6 (1, 4096)
fc7 (1, 4096)
fc8 (1, 1000)
prob (1, 1000)
1 | for layer_name, param in net.params.iteritems(): |
conv1 (96, 3, 11, 11) (96,)
conv2 (256, 48, 5, 5) (256,)
conv3 (384, 256, 3, 3) (384,)
conv4 (384, 192, 3, 3) (384,)
conv5 (256, 192, 3, 3) (256,)
fc6 (4096, 9216) (4096,)
fc7 (4096, 4096) (4096,)
fc8 (1000, 4096) (1000,)
1 | def vis_square(data): |
1 | # the parameters are a list of [weights] |
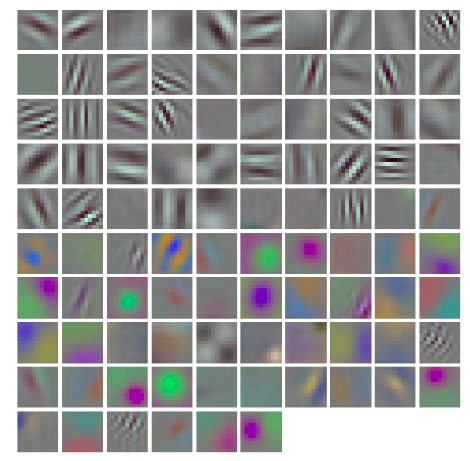
1 | vis_square(filters[:96].reshape(96**3, 11, 11)) |
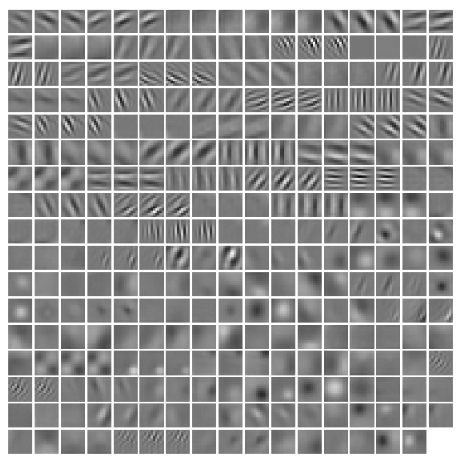
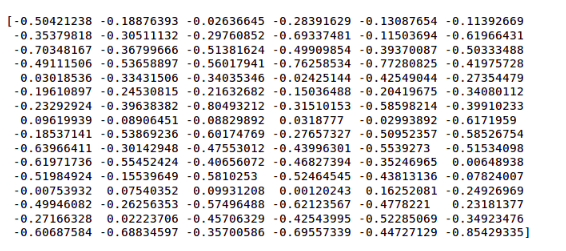
1 | # the parameters are a list of biases |
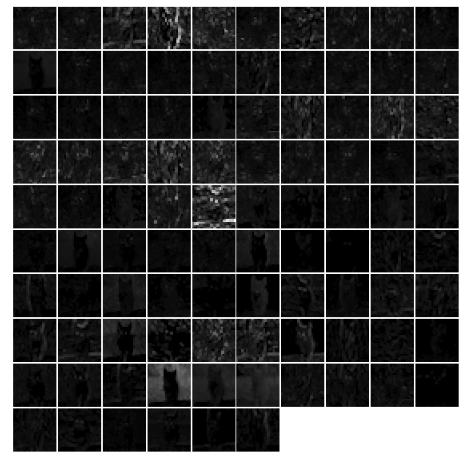
1 | # show the output after conv1 layer |

1 | # show the output after pool1 layer |
1 | # show the output after norm1 layer |
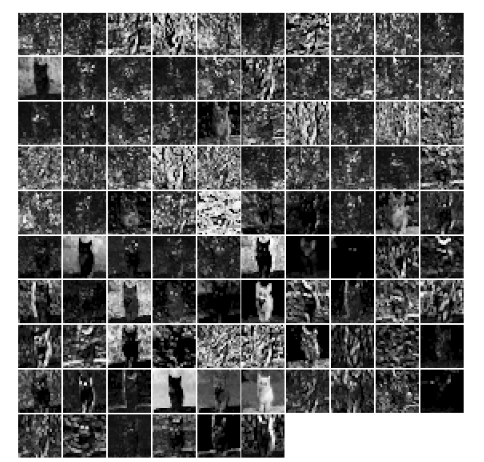
1 | # the parameters are a list of weights in conv2 layer |
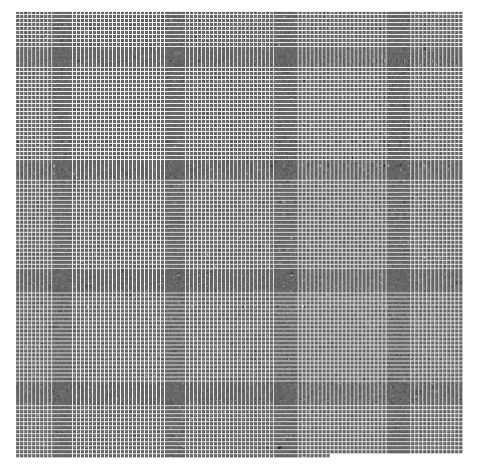
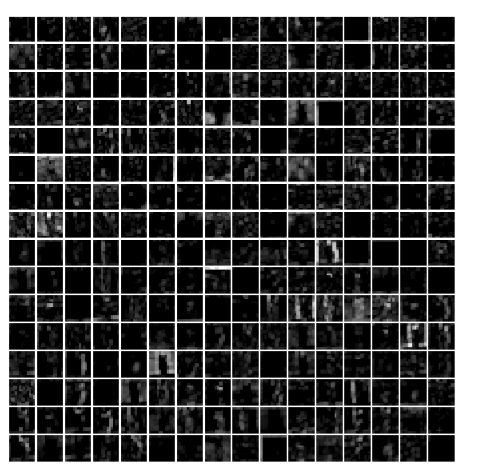
1 | # the parameters are a list of biases. |

1 | # show the result after conv2 |
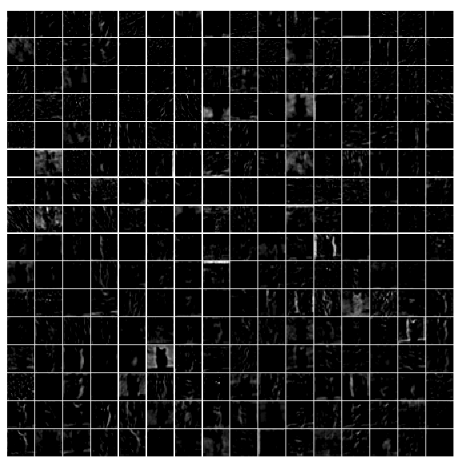
1 | # show the result after pooling2 |

1 | # show the result after LRN |

1 | # show the result after conv3 |
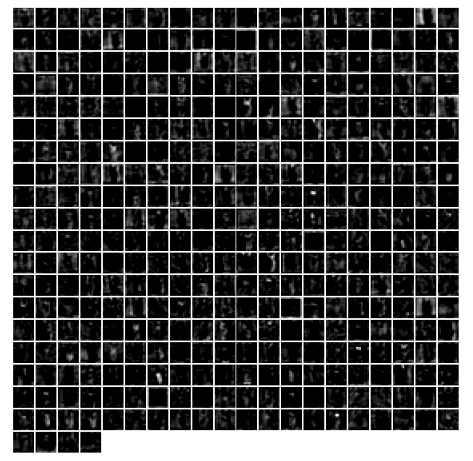
1 | # show the result after conv4 |
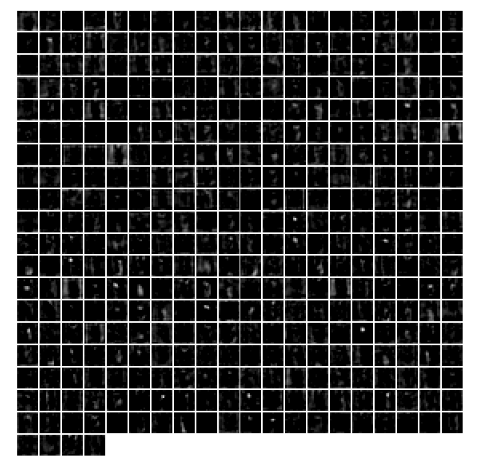
1 | # show the result after conv5 |
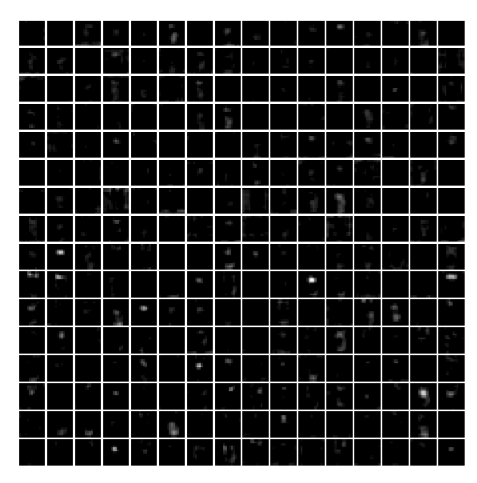
1 | # show the result after pooling layer 5 |
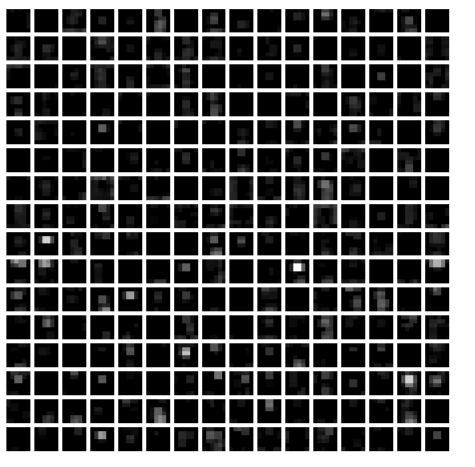
1 | # show the result after fc6 layer |
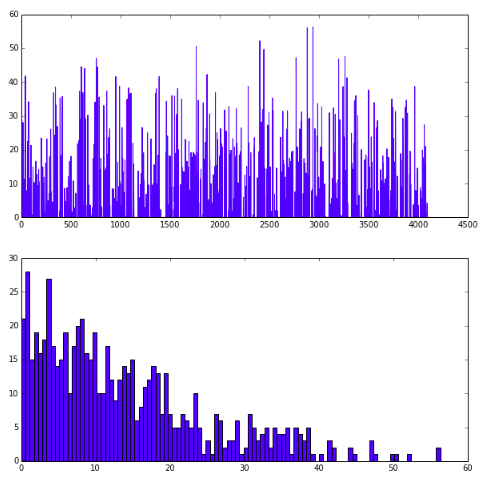
1 | # show the result after fc7 |
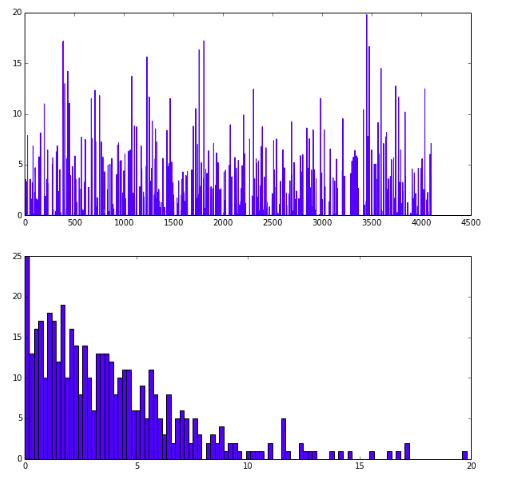
1 | # show the result after fc8 |
1 | # show the result after prob layer |
Loss 和accuracy可视化
1 | import numpy as np |
如果不需要绘制曲线,只需要训练出一个caffemodel, 直接调用solver.solve()就可以了。如果要绘制曲线,就需要把迭代过程中的值
保存下来,因此不能直接调用solver.solve(), 需要迭代。在迭代过程中,每迭代200次测试一次
1 | %%time |
Iteration 0 testing… accuracy: 0.10000000149
Iteration 200 testing… accuracy: 0.419999986887
Iteration 400 testing… accuracy: 0.479999989271
Iteration 600 testing… accuracy: 0.540000021458
Iteration 800 testing… accuracy: 0.620000004768
Iteration 1000 testing… accuracy: 0.629999995232
Iteration 1200 testing… accuracy: 0.649999976158
Iteration 1400 testing… accuracy: 0.660000026226
Iteration 1600 testing… accuracy: 0.660000026226
Iteration 1800 testing… accuracy: 0.670000016689
Iteration 2000 testing… accuracy: 0.709999978542
Iteration 2200 testing… accuracy: 0.699999988079
Iteration 2400 testing… accuracy: 0.75
Iteration 2600 testing… accuracy: 0.740000009537
Iteration 2800 testing… accuracy: 0.769999980927
Iteration 3000 testing… accuracy: 0.75
Iteration 3200 testing… accuracy: 0.699999988079
Iteration 3400 testing… accuracy: 0.740000009537
Iteration 3600 testing… accuracy: 0.72000002861
Iteration 3800 testing… accuracy: 0.769999980927
1 | print test_acc |